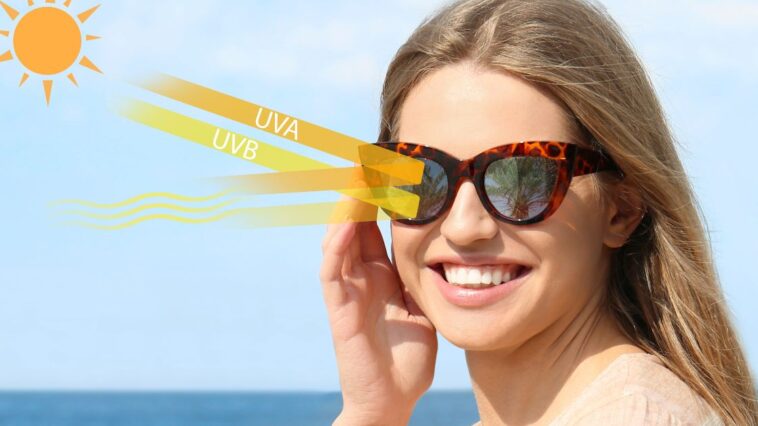
Our eyes are incredibly delicate and vulnerable to damage from various external factors. One of the most significant threats to our eyes is the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can lead to various eye problems, including cataracts, macular degeneration, and even cancer.
Fortunately, we can protect our eyes by taking preventive measures, with sunglasses being a crucial tool in our defense against UV radiation. In this article, we will delve into the effects of UV radiation on the eyes, understand the importance of sunglasses, and explore how to protect your eyes from UV damage effectively.
Understanding UV Radiation
Ultraviolet radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. It is categorized into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC, based on their wavelength and energy levels. While the Earth’s ozone layer primarily blocks UVC rays, UVA and UVB rays can still penetrate the atmosphere and cause harm to our eyes and skin.
UVA rays have the longest wavelength and the lowest energy among the three types. They are present throughout the day, regardless of weather conditions. UVA rays can penetrate the eye and are associated with the development of cataracts and macular degeneration.
UVB rays have shorter wavelengths and higher energy than UVA rays. They are particularly intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. and more prevalent in summer. UVB rays primarily affect the front part of the eye, leading to conditions such as corneal sunburn (photokeratitis), cataracts, and growths on the eye’s surface.
The Effects of UV Radiation on the Eyes
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can have severe consequences for our eyes. Let’s explore some of the eye conditions associated with UV damage:
- Cataracts are characterized by clouding the eye’s natural lens, leading to blurred vision and eventual vision loss. UVA and UVB radiation have been linked to the development and progression of cataracts.
- Macular Degeneration: UV radiation can contribute to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) development, particularly UVA rays. AMD affects the central part of the retina, leading to a gradual loss of central vision.
- Photokeratitis: Also known as “snow blindness” or “welder’s flash,” photokeratitis occurs due to excessive exposure to UVB rays. It causes painful inflammation of the cornea, leading to temporary vision loss, redness, and sensitivity to light.
- Pterygium: Pterygium is a growth of tissue on the white of the eye (conjunctiva) that can extend onto the cornea. UV radiation and other environmental factors are believed to contribute to the developing of pterygium.
The Importance of Sunglasses for UV Protection
Given the detrimental effects of UV radiation on our eyes, it is crucial to take proactive steps to protect them. Sunglasses play a vital role in shielding our eyes from harmful UV rays. Let’s explore the reasons why sunglasses are essential for UV protection:
- UV Ray Blocking: High-quality sunglasses are designed to block 100 percent of both UVA and UVB rays. When purchasing sunglasses, look for labels or markings indicating their UV protection level. Opting for sunglasses with UV400 protection ensures that they block wavelengths up to 400 nanometers, covering the entire spectrum of UVA and UVB rays.
- Reduction of Glare: Sunglasses with polarized lenses effectively reduce glare caused by reflections from shiny surfaces such as water, snow, and roads. Glare causes discomfort and increases the risk of accidents and eyestrain. By minimizing glare, polarized sunglasses improve visibility and enhance overall eye comfort.
- Protection from High-Energy Visible (HEV) Light: In addition to UV radiation, sunglasses can also offer protection against high-energy visible (HEV) light, often referred to as “blue light.” Digital screens, fluorescent lighting, and the sun emit HEV light. Prolonged exposure to HEV light has been linked to eye strain, fatigue, and potential long-term damage to the retina. Certain sunglasses are designed with lenses that block or reduce HEV light, providing added protection.
- Preservation of Eye Health: By wearing sunglasses consistently, we can significantly reduce the risk of eye conditions associated with UV damage. Protecting our eyes from harmful UV rays and minimizing exposure to glare and HEV light can help preserve long-term eye health, ensuring clear vision and minimizing the risk of developing serious eye problems.
Choosing the Right Sunglasses
When selecting sunglasses for optimal UV protection, consider the following factors:
- UV Protection: Ensure that your sunglasses provide 100 percent UV protection. Look for labels or markings indicating the level of UV protection the lenses offer.
- Lens Material: Sunglasses can be made from various materials, including glass, polycarbonate, and acrylic. Polycarbonate lenses are lightweight, impact-resistant, and offer excellent UV protection, making them a popular choice for sunglasses.
- Lens Color: The color of the lenses does not determine the level of UV protection. However, different lens tints can enhance visual comfort in specific environments. For example, gray lenses provide natural color perception and are suitable for general outdoor activities, while brown lenses enhance contrast and are ideal for sports and outdoor pursuits.
- Fit and Coverage: Sunglasses should fit properly and provide adequate coverage to protect the eyes from UV rays entering from the sides. Consider sunglasses with a wraparound style or larger frames to ensure maximum coverage and minimize peripheral exposure to UV radiation.
Additional UV Protection Measures
While sunglasses are essential for protecting our eyes from UV damage, they are not the only measure we should take. Here are some additional steps to enhance UV protection:
- Wide-Brimmed Hats: Wearing a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses can provide additional shade and protect the delicate skin around the eyes from UV radiation. This combination offers comprehensive protection to both the eyes and surrounding areas.
- Sunscreen for the Face: Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) to the face, including the eyelids, further protects the skin and reduces the risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
- Time and Environment: Minimize outdoor activities during peak sunlight hours when UV radiation is most intense, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Seek shade whenever possible, especially in environments with highly reflective surfaces such as snow, sand, or water.
- UV Protection for Children: Children’s eyes are particularly susceptible to UV damage, as their lenses are clearer and their exposure to sunlight is often greater. Encourage children to wear sunglasses with proper UV protection and accompany them with hats for complete UV coverage.
Conclusion
Protecting our eyes from the harmful effects of UV radiation is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health and preventing eye conditions associated with prolonged sun exposure.
Sunglasses provide:
- A vital defense against UV rays.
- Offering UV protection.
- Glare reduction.
- Shielding from HEV light.
When selecting sunglasses, prioritize those that provide 100 percent UV protection and consider factors such as lens material, tint, fit, and coverage. Remember to complement sunglasses with wide-brimmed hats, sunscreen, and mindful exposure to sunlight. By adopting these preventive measures, we can enjoy the outdoors while safeguarding our precious vision for years.