What is Blepharitis?
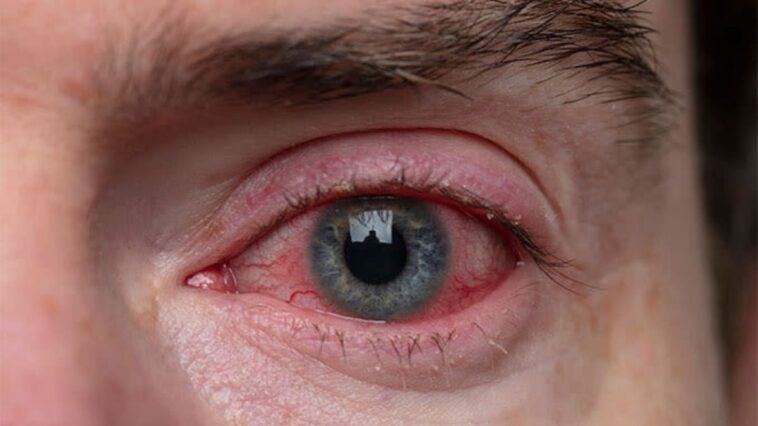
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids, affecting the skin and eyelash hair follicles. It is characterized by red, itchy, and sometimes swollen eyelids, with a sensation of burning or foreign body in the eye.
It may also cause eyelash loss and crusting along the eyelashes and eyelid margins. The exact cause of blepharitis is often unclear, but bacteria, skin conditions, oil gland dysfunction, and other factors can cause it.
What are the Causes of Blepharitis?
Blepharitis can be caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Bacteria: Overgrowth of the bacteria Staphylococcus can cause inflammation in the eyelids.
- Oil Gland Dysfunction: Blockages in the meibomian glands that produce oil for the tears can cause the oil to become thick and stagnant, leading to inflammation.
- Skin Conditions: Dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, and rosacea can cause eyelid inflammation.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to cosmetics, contact lenses, or environmental irritants can cause inflammation in the eyelids.
- Demodex mites: Tiny mites that naturally live on the skin can cause eyelid irritation and inflammation.
- Other factors: Certain medical conditions like lupus, thyroid disorders, and facial nerve disorders can cause blepharitis.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
The common symptoms of blepharitis include:
- Itching, burning, or redness in the eyes
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Formation of crusty debris along the eyelashes
- Irritation and burning sensation along the eyelids
- Styes, small painful lumps on the eyelid
- Eyelash loss or permanent damage to the eyelashes
- Dry eyes or excessive tearing
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen, as untreated blepharitis can lead to more severe eye problems.
Conditions Associated with Blepharitis
Blepharitis can be associated with the following conditions:
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Blepharitis can cause the eyelid’s oil glands to produce poor-quality oil, leading to dry eyes.
- Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear tissue covering the white part of the eye, can occur due to blepharitis.
- Stye: A stye is a common eye condition characterized by an inflamed, red bump on the eyelid’s edge. It is often caused by blepharitis and can be quite painful.
- Corneal complications: Inflammation and irritation caused by blepharitis can lead to corneal complications, such as scarring and vision loss.
- Rosacea is a prevalent skin condition that mainly affects the face. It causes redness, swelling, and sometimes small, red bumps on affected areas. Rosacea can cause inflammation in the face, including on the eyelids, leading to blepharitis
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This skin condition can cause dandruff and red, scaly patches on the skin, including the eyelids, leading to blepharitis.
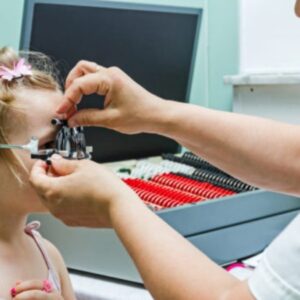
How Is Blepharitis Diagnosed?
Blepharitis is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, which includes the following steps:
- Medical history review: The eye doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and previous eye conditions.
- The visual acuity test is a test to measure your ability to see clearly at different distances.
- Eye exam: The eye doctor will examine the external and internal structures of the eye, including the eyelids and the tear film.
- Slit lamp examination: A special microscope is used to examine the eyelids and tear film in detail.
- Meibomian gland evaluation: The eye doctor will gently press on the eyelid to assess the function of the meibomian glands and the quality of the oil they produce.
Based on the eye exam results, the eye doctor may perform additional tests, such as a culture of the eyelid or a tear film analysis, to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of eyelid inflammation.
Treatment and Prevention of Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and treatment. The following methods can help treat and prevent blepharitis:
- Lid Hygiene: Cleaning the eyelids regularly is essential to maintaining healthy eyes. To do this, use a warm, damp cloth to wipe away any excess oil and debris gently. Doing so can aid in preventing inflammation and other problems associated with poor lid hygiene.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections. In the case of blepharitis, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to kill any bacteria contributing to this condition.
- Medicated Eye Drops: Medicated Eye Drops are eye drops that provide relief from dry or irritated eyes. These drops contain artificial tears and lubricants to help keep eyes moistened and comfortable. They can offer a quick fix for symptoms of dryness, redness, discomfort, and more.
- Warm Compresses: Regularly applying a warm, moist compress to the eyelids is a beneficial way to soften and express the oils in meibomian glands. This can be done several times each day for optimal results.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acid supplements may help improve the quality of the oil produced by the meibomian glands and reduce inflammation.
- Allergy Management: Avoiding known allergens and using antihistamines or other allergy medications can help manage blepharitis caused by allergies.
- Skin Condition Management: Treating underlying skin conditions like dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis can help reduce inflammation and prevent blepharitis.
It is vital to follow your eye doctor’s instructions and continue treatment even when symptoms improve to prevent flare-ups and maintain good eyelid health.
Does Poor Hygiene Cause Blepharitis?
Poor hygiene is not the direct cause of blepharitis, but it can sometimes contribute to the condition. For example, if the eyelids are not adequately cleaned and bacteria are allowed to accumulate, this can increase the risk of infection and inflammation. Additionally, a buildup of oil and debris on the eyelids can also contribute to the development of blepharitis.
However, it is essential to note that many other factors can contribute to the development of blepharitis, including bacterial infections, skin conditions, hormonal imbalances, clogged oil glands, allergies, and lid margin abnormalities.
Maintaining good hygiene is vital for overall eye health and can help to prevent the worsening of blepharitis symptoms, but it is not a direct cause of the condition.
How Long Does it Take for Blepharitis to Go Away?
The duration of blepharitis depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the individual’s response to treatment. Blepharitis can sometimes resolve quickly with proper treatment and good hygiene within days or weeks.
However, for some people, blepharitis can be a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. In these cases, symptoms may come and go or persist even with proper treatment. In some cases, blepharitis may also recur even after effectively managing it.
It is essential to work closely with an eye doctor or ophthalmologist to determine the best course of treatment for the individual case of blepharitis. With proper care and attention, it is possible to manage blepharitis’s symptoms and improve the eyes’ overall health.
When to See An Eye Doctor
You should seek medical advice for blepharitis if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Persistent or worsening eye irritation, redness, or burning
- Pain or swelling in the eyelids
- Blurred or double vision
- Recurrent styes or chalazion (swollen lumps on the eyelid)
- Eyelash loss or irregular growth
- Sensitivity to light or increased tearing
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
See a doctor promptly if you experience any sudden changes in vision or eye pain, as this may indicate a more serious eye condition. Regular eye exams can help monitor the progress of blepharitis and ensure prompt treatment if symptoms worsen or new symptoms develop.
Conclusion
Blepharitis is a common condition that affects the eyelids and can cause various symptoms, including redness, itching, burning, and crusting. Various factors, including bacterial infections, skin conditions, hormonal imbalances, clogged oil glands, allergies, and lid margin abnormalities, can cause it.
Diagnosing blepharitis is performed through a comprehensive eye exam, and treatment may include warm compresses, lid scrubs, antibiotics, artificial tears, medications, and lifestyle changes.
The duration of blepharitis can vary, and it may be a chronic condition that requires ongoing management.
Good hygiene and prompt treatment of any underlying conditions can help prevent the development of blepharitis and improve the eyes’ overall health.