When contemplating the delicate structure of the human eye, many people think of the lens, cornea, and retina. However, one important component that frequently goes unrecognized is the vitreous humor. This clear, gel-like liquid covers the space between the lens and the retina, helping to keep the eye in form and functioning properly. We will examine the role of vitreous humor, its significance for ocular health, and the consequences of disrupting its balance in this comprehensive tutorial.
What is vitreous humor?
Vitreous humor is a clear, gel-like liquid that fills the vitreous cavity, which is located between the lens and the retina. In contrast to the constant creation and draining of aqueous humor, vitreous humor forms during early development and remains relatively stable throughout life. Water makes up 98-99% of the vitreous humor, but it also contains collagen fibers, hyaluronic acid, and other proteins that contribute to its gel-like consistency.
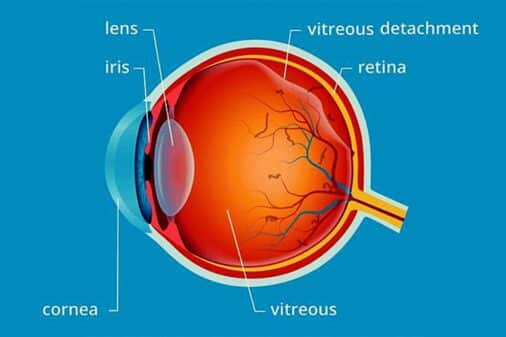
The primary functions of vitreous humor
The vitreous humor may not be as dynamic as the aqueous humor, but it performs several crucial processes that are essential for the eye’s health and functionality.
- Maintaining Eye Shape
The vitreous humor plays a critical role in maintaining the eye’s spherical shape. This gel-like substance fills the vitreous cavity, exerting slight outward pressure to keep the eyeball tight and round. This structural support is essential since any modification of the eye’s shape might result in refractive defects like myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness).
- Supporting the retina
The vitreous humor supports the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light into neural messages. The vitreous humor forces the retina against the choroid (a layer rich in blood vessels), keeping it connected and in the proper position. This is critical for maintaining clear and focused vision, as any retinal detachment or displacement can cause major visual problems.
- Light Transmission.
Despite not directly refracting light like the cornea or lens, the vitreous humor plays a crucial role in its transmission. Because the vitreous humor is clear, light can pass through unhindered and reach the retina with minimal distortion. This clarity is critical to ensuring that the images projected onto the retina are sharp and clear.
- Shock absorption.
The vitreous humor also serves as a shock absorber for the eyes. Because of its gel-like consistency, it can cushion the eye against mild hits and motions, preserving the delicate structures within the eye, particularly the retina, from any harm. This function is especially crucial during activities that require quick movements or slight injuries to the head or face.
- Establishing a nutritional pathway
While the vitreous humor does not directly supply nutrients like the aqueous humor, it does contribute to eye health by acting as a channel for nutrients and waste materials. The vitreous humor’s gel-like nature allows important nutrients, such as oxygen and glucose, to diffuse to surrounding tissues, particularly the retina. This procedure helps to keep the retina healthy and operating properly.
Common Conditions Related to Vitreous Humor
Although the vitreous humor is usually constant throughout life, certain circumstances might alter its composition or function, resulting in visual disturbances or other eye problems.
Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD)
Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is one of the most prevalent age-related alterations to the vitreous fluid. As we age, the vitreous humor begins to liquefy and shrink, causing it to separate from the retina. While PVD is typically harmless and a normal part of aging, it can cause symptoms such as floaters and flashes of light. In some circumstances, PVD can raise the risk of retinal detachment, a dangerous condition that necessitates prompt medical attention.
vitreous hemorrhage
A damaged blood vessel in the retina is typically responsible for vitreous hemorrhage, which occurs when blood escapes into the vitreous humor. This disorder can produce significant visual abnormalities, such as the rapid appearance of floaters or a sharp decrease in vision. Various conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy, trauma, or retinal vein obstruction, can cause vitreous hemorrhage. The treatment depends on the underlying reason and may include laser therapy or surgery to remove the blood and restore clear eyesight.
Vitreous Detachment
In some situations, the vitreous humor might separate from the retina, resulting in a condition known as vitreous detachment. This might happen naturally as we age or as a result of trauma. Symptoms of vitreous detachment include an increase in floating and flashes of light, which are comparable to PVD. While vitreous detachment is normally harmless, it can occasionally result in more significant consequences, such as retinal tears or detachment, which require immediate treatment.
Macular Hole
A macular hole is a small break in the macula, the core region of the retina that allows for fine, detailed vision. This syndrome occurs when the vitreous humor moves away from the retina but remains linked to the macula, creating stress and causing the macula to rip. A macular hole can cause clouded or distorted central vision, necessitating surgical intervention for correction.
Vitreous floaters
Vitreous floaters are tiny, shadowy forms that emerge in your field of vision and frequently move when you try to look at them. Typically, the vitreous humor generates small clumps of collagen fibers that form shadows on the retina. An eye care specialist should investigate a sudden rise in floaters or the appearance of flashes of light, as they may indicate a more serious condition, such as retinal detachment.
Diagnosing Vitreous Humor Conditions.
An accurate identification of vitreous humor disorders is critical for optimal management and treatment. Eye care specialists employ a variety of diagnostic tools and techniques to evaluate the health of the vitreous fluid and identify any anomalies.
Eye Exam
A thorough eye exam is the first step in detecting vitreous fluid disorders. During the exam, the eye care specialist will dilate your pupils and check the vitreous cavity and retina with sophisticated devices like an ophthalmoscope or slit lamp. This enables them to detect any evidence of vitreous detachment, bleeding, or other abnormalities.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique for obtaining comprehensive cross-sectional pictures of the retina and vitreous cavity. OCT is very beneficial for detecting macular holes, retinal detachment, and other structural changes in the eye. It enables the eye care practitioner to see the layers of the retina in excellent detail, making it easier to diagnose and assess any abnormalities.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasonography imaging can reveal the retinal and vitreous cavities when blood or other opacities obscure the vitreous humor. Ultrasound is excellent for detecting retinal detachments or vitreous hemorrhages that are not evident with other imaging methods.
Treatment for Vitreous Humor-Related Conditions
The exact diagnosis and severity of the problem dictate the treatment and management of vitreous humor disorders. Treatment often aims to reduce symptoms and avoid consequences.
Observation
Minor problems, like vitreous floaters or moderate PVD, may only require observation and regular monitoring. Over time, the brain adapts to floaters, making them less visible. However, it is critical to have frequent eye exams to ensure that no more serious diseases arise.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is a surgical technique that removes the vitreous humor and replaces it with a saline solution or gas bubble. More serious diseases like vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, and macular holes commonly require this surgery. When other therapies fail, a vitrectomy can help restore vision by eliminating opacities or tension on the retina.
Laser Treatment
Treatment for vitreous humor issues, including retinal tears and minor retinal detachments, can involve laser therapy. By generating small burns surrounding the tear or separation, the laser can help seal the retina to the underlying tissue, preventing the problem from progressing further.
Preventing Vitreous Humor Conditions
Some changes to the vitreous humor, like PVD, are unavoidable with age, but you can reduce your risk of more serious issues.
Regular eye examinations
Regular eye exams are critical for recognizing abnormalities in the vitreous fluid and retina early on, allowing for timely treatment if necessary. If you notice any rapid changes in your vision, such as more floaters, flashes of light, or a shadow across your vision, you should seek medical assistance right away.
Protecting your eyes.
Protecting your eyes from trauma is also critical for avoiding vitreous humor problems. Wearing protective eyewear during potentially hazardous activities, such as sports or certain vocations, can help lower the risk of vitreous detachment or hemorrhage.
Managing underlying health conditions.
Managing underlying health issues, including diabetes or high blood pressure, is also critical for keeping your eyes healthy and avoiding vitreous fluid complications. Regular check-ups with your healthcare practitioner can help you manage these disorders and lower your risk of eye problems.
Conclusion
The vitreous humor may not be as well-known as other sections of the eye, yet its role in ocular health is critical. The functions of vitreous humor, which include supporting the retina, maintaining the shape of the eye, and transferring light, are critical for clear and healthy vision.
Understanding its importance and identifying the indicators of vitreous humor-related diseases allows you to take proactive efforts to protect your eyesight and keep your eyes healthy for years to come. Regular eye exams, early detection, and proper management of underlying health concerns are essential for ensuring that your vitreous humor continues to sustain your vision throughout your lifetime.