What Is A Stye?
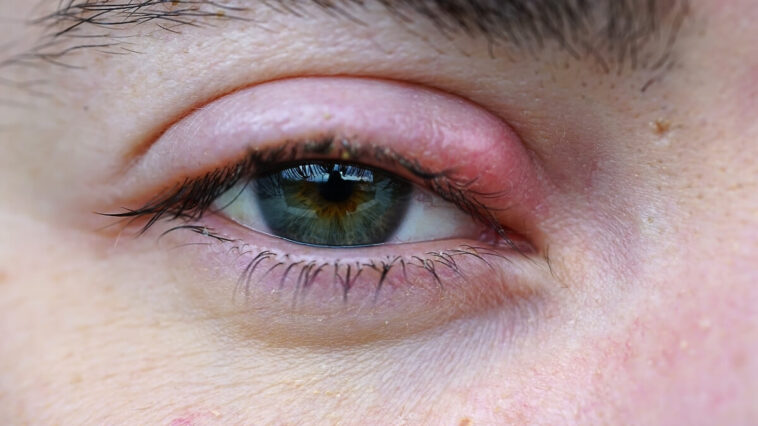
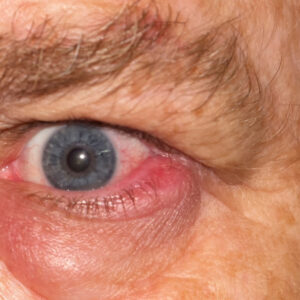
A stye is a small, painful lump that appears on the eyelid. An infection causes it in one of the glands of the eyelid. The infection can be caused by bacteria that live on the skin, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
Styes typically appear as red, swollen bumps on the eyelid and may be accompanied by pain, tenderness, and swelling. They can be located on the inner or outer part of the eyelid and may be accompanied by a discharge of pus.
Styes are usually not severe and can be treated with warm compresses and over-the-counter pain medication. In some cases, antibiotics may be needed to clear the infection. It is essential to keep the area clean and avoid touching or rubbing the infected eyelid, as this can spread the infection or cause the stye to rupture. If the stye persists for more than several days or if it is causing significant discomfort, it is a good idea to see an ophthalmologist.
What Causes a Stye?
A stye is a small, painful bump appearing on the eyelid’s edge, usually near the lashes. A blockage causes it in one of the small oil glands in the eyelid. A stye can be red and swollen and may cause tearing, sensitivity to light and a feeling of grit in the eye.
A stye can be caused by a number of different factors. These include:
- Poor hygiene: Not correctly cleaning the eyelids and surrounding area can allow bacteria to grow and lead to an infection.
- Stress can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can increase the risk of developing a stye.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids), can increase the risk of developing a stye.
- Using contaminated makeup: Using contaminated makeup or not properly cleaning makeup brushes can increase the risk of developing a stye.
- Trauma: Trauma to the eyelid, such as rubbing the eye or wearing contact lenses, can increase the risk of developing a stye.
Signs and Symptoms?
The main signs and symptoms of a stye include:
- A small, painful lump on the eyelid
- Redness and swelling of the affected eyelid
- Tenderness or pain in the area
- A discharge of pus from the affected eyelid
- Swelling of the surrounding skin
- Difficulty opening the eye due to swelling and tenderness
In some cases, a stye may cause a feeling of pressure or a sensation of something in the eye. Some people may also experience watery eyes or sensitivity to light.
If you think you have a stye, it is essential to seek medical attention quickly. The eye doctor can properly diagnose and treat the condition. Refrain from touching or rubbing the affected area, as this may cause the infection to spread or for the stye to rupture.
Where Can You Get A Stye?
Styes are most commonly found on the outer part of the eyelid, near the eyelashes. They may also occur on the inner part of the eyelid, closer to the eye.
It is possible for an individual to experience multiple styes simultaneously.
Styes are not contagious, so getting a stye from someone else is impossible. Styes, which are caused by bacteria, can be transmitted from person to person through close contact or the sharing of items like towels and makeup.
Practicing good hygiene, including washing your hands regularly and not sharing personal items, is essential to help prevent infection.
How to Get Rid of a Stye?
There are a variety of treatments you can use to get rid of a stye:
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the area several times a day can help reduce inflammation and support drainage. The compress is an easy DIY, soak a clean cloth in warm water and hold it on the spot for 5-10 minutes. Doing this regularly may help clear up the stye more quickly.
- Over-the-counter pain medication: Taking over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with a stye.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection causing the stye.
- Eyelid hygiene: Keeping the affected eyelid clean and avoiding contact with the stye can help prevent the spread of infection. Avoid touching or rubbing the stye, and wash your hands frequently.
- Avoiding contaminated makeup: Using or not properly cleaning makeup brushes can increase the risk of developing a stye. To prevent this, clean your makeup brushes regularly and toss any makeup past its expiration date.
If a stye persists or is causing severe discomfort, it is essential to seek medical attention, as treatment may involve draining or surgical removal. Sometimes, a stye may need to be drained or removed surgically.
Are Styes Contagious?
Styes are not contagious. They are caused by an infection in one of the eyelid glands and are not transmitted from person to person through direct contact or proximity.
However, the bacteria that cause styes, such as Staphylococcus aureus, can be transmitted from person to person through close contact or by sharing items such as towels or makeup.
Good hygiene is an essential part of preventing the spread of infections, such as stye. Washing your hands frequently and not sharing personal items are both key steps in avoiding the contraction and transmission of a stye.
If you have a stye, avoiding touching or rubbing the affected area is essential, as this can spread the infection or cause the stye to rupture. If you suspect a stye, seeing an ophthalmologist for proper diagnosis and treatment is a good idea.
How To Prevent Styes?
If you’re worried about developing a stye, here are some helpful tips you can follow to reduce your risk:
- Practice good hygiene: Clean your eyelids regularly with mild soap and warm water. Avoid sharing towels, washcloths, or makeup with others.
- Avoid contaminated makeup: Always use clean makeup and makeup brushes, and replace them regularly.
- Remove contact lenses properly: Follow the instructions for cleaning and removing your contact lenses to reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes: Rubbing your eyes can irritate the eyelids and increase the risk of infection.
- Avoid wearing eye makeup if you have an active stye: If you have a stye, avoid wearing eye makeup or using contact lenses until the stye has entirely resolved.
- Get enough sleep: An inadequate amount of rest can weaken the body’s immunity, making it more susceptible to infection and increasing the risk of developing a stye.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infection.
By following these steps, you can help to reduce your risk of developing a stye. If you suspect you have a stye, it is a good idea to see an ophthalmologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How Long Does a Stye Last?
How long a stye last depends on several factors, including the cause of the stye and the individual’s immune system. In most cases, a stye will resolve independently within a few days to a week with proper treatment.
To help reduce the duration of a stye, it is essential to apply warm compresses to the affected area several times a day and keep it clean. Over-the-counter pain medication may also help reduce pain and inflammation. If a stye persists for more than several days, it may indicate infection, and medical attention should be sought.
It is essential to avoid squeezing or attempting to drain the stye on your own, as this can cause the infection to spread or lead to further complications. If you have a stye, avoiding touching or rubbing the affected area is essential, as this can spread the infection or cause the stye to rupture.
What Is A chalazion?
A chalazion is a small, painless lump that appears on the eyelid. It is caused by a blockage in one of the small oil glands that produce oil to lubricate the eye. A chalazion typically appears as a small, firm lump on the eyelid and is usually not painful.
It is essential to understand the difference between a chalazion and stye in order to receive proper treatment.
A chalazion is usually located on the inner part of the eyelid. It is not painful, while a stye is usually located on the outer part of the eyelid and is painful. A doctor can properly diagnose and recommend treatment for a chalazion or a stye.
Chalazion treatments
Treatment of a chalazion may include:
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes several times a day can help soften the gland’s blockage and reduce inflammation.
- Gentle massage: Gently massaging the affected area with a clean finger can help to unclog the blocked gland.
- Use of lubricating eye drops: Using lubricating eye drops or ointments can help to moisten the eye and reduce inflammation.
- Use of topical medications: Topical medications, such as corticosteroid creams or ointments, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Drainage: In some cases, a chalazion may need to be drained by an eye doctor. This is typically done by making a small incision in the chalazion and draining the contents.
- Antibiotics: If an infection causes the chalazion, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
Following the treatment plan recommended by your eye doctor to help resolve the chalazion and prevent a recurrence is essential. If the chalazion is causing discomfort or vision problems, it is a good idea to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to See an Eye Doctor
If you have a stye, you must see an ophthalmologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. It is imperative to see an eye doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- The stye is accompanied by fever, redness, or swelling around the eye
- The stye is causing significant discomfort or pain
- The stye persists after a few days
- The stye is accompanied by vision changes or other abnormalities in the eye
In some cases, a stye may signify a more serious underlying condition, such as an infection or an immune system disorder. A doctor can properly diagnose and treat any underlying conditions and help to prevent further complications.
It is important to avoid squeezing or attempting to drain the stye on your own, as this can cause the infection to spread or lead to further complications. If you have a stye, avoiding touching or rubbing the affected area is essential, as this can spread the infection or cause the stye to rupture.